DFW Cross Docking Services (Last Mile, Local Delivery, Local Distribution)
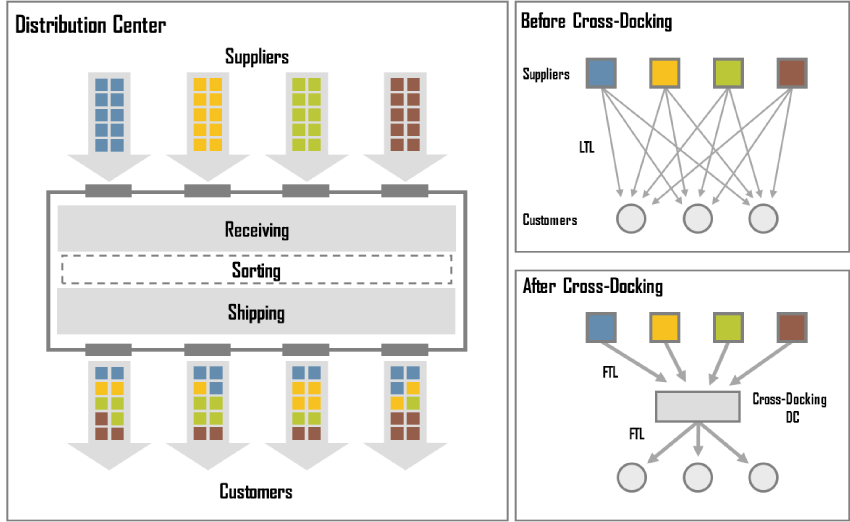
Cross-docking is a practice in logistics of:
– unloading materials from an incoming semi-trailer truck or railroad car
– loading these materials directly into outbound trucks, trailers, or rail cars,
with little or no storage in between.
Cross docking also has many other names or related services.
– Container Break, or container breakdown.
– Container unloading, sorting, loading.
– Local Distribution / Last Mile Delivery Services / Local Delivery
Reasons for applying cross docking are:
– to change type of conveyance
– to sort material intended for different destinations
– to combine material from different origins into transport vehicles (or containers)
with the same, or similar destination.
In the LTL trucking industry, cross-docking is done by moving cargo from one transport vehicle directly into another, with minimal or no warehousing. In retail practice, cross-docking operations may utilize staging areas where inbound materials are sorted, consolidated, and stored until the outbound shipment is complete and ready to ship.
When is cross-docking used?
The process of cross docking will not suit every warehouses needs, it is therefore important to make an informed decision as to whether cross-docking will increase the productivity, costs and customer satisfaction for your specific business. Cross docking can advance the supply chain for a variety of specific products. For one, unpreserved or temperature controlled items such as food which need to be transported as quickly as possible can be benefitted by this process. Additionally, already packaged and sorted products ready for transportation to a particular customer can become a faster and more efficient process through cross docking.
Some of the main reasons cross docking is implemented is to:
- Provide a central site for products to be sorted and similar products combined to be delivered to multiple destinations in the most productive and fastest method. This process can be described as “hub and spoke”
- Combine numerous smaller product loads into one method of transport to save on transportation costs. This process can be described as ‘consolidation arrangements’.
- Break down large product loads into smaller loads for transportation to create an easier delivery process to the customer. This process can be described as ‘deconsolidation arrangements’.